Dendritic polymer is a kind of branched polymer with high symmetry. Its peripheral chain segment increases at exponential level with algebraic-level increase of compound. It is of accurate molecular structure. There is cavum in the molecule, and the molecule itself is of nanometer dimension, its functional group can achieve function of the molecule in the core of compound and peripheral modification. These unique features allow dendritic polymer to be adopted to simulate optical trapping system in photosynthesis. Compared with finished structure of natural biology system, there are large amount of optical trapping groups compactly accumulating at molecule exterior at periphery of dendritic polymer. Moreover, degree of freedom of conformation of molecule framework is rather high, which makes more mutual action between peripheral groups, which will lead to dissipation of trapping energy. It is one of hotspots for current research on how to reduce the energy loss and improve the performance of optical trapping dendritic polymer.
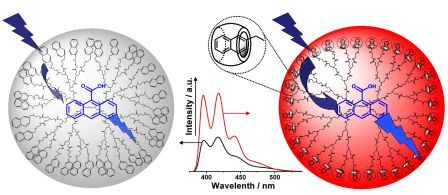
With great support of National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China and China Academy of Science (CAS), researchers of synthesis photochemistry experiment team of Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, CAS have made studies on energy transfer and electron transfer in optical trapping system of dendritic polymer in recent years, and series of innovative achievements have been obtained(J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 2165-2171; J. Phys. Chem., B, 2006, 110, 4047-4053 and 4663-4670; Macromolecules, 2007,40, 9384-9390, etc ). Recently, researchers of this team have designed and synthesized series of peripheral modification naphthalene PAMAM dendritic polymer, optical trapping dendritic polymer with pseudorotaxane structure is gained through non-covalent modification of Cucurbituril to peripheral naphthalene group of dendritic polymer. This non-covalent modification is of reversibility and can effectively restrain energy dissipation caused by mutual action between peripheral naphthalene groups, increase luminescence quantum yield of dendritic polymer and energy transfer efficiency from peripheral group to energy receptor, thus to increase the utilization rate of energy in optical trapping system. Related research results have been published in “Journal of the American Chemical Society”》(J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9100-9106). This research provides new approach for developing new controllable optical trapping and photoluminescence dendritic polymer. |

