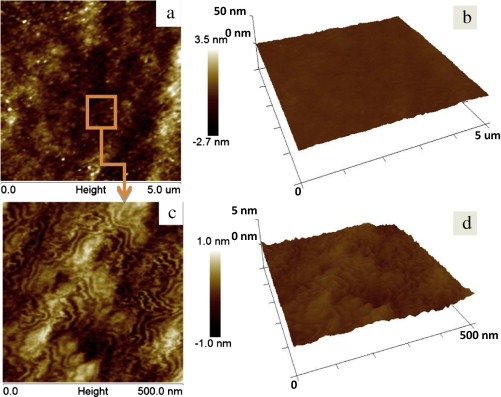
(a, c) Two- and (b, d) three-dimensional AFM images of microporous silica coating prepared on PMMA substrate by a withdrawing speed of 5 cm/min from HCl-catalyzed silica sol with 3.5 wt% CTAB and post-treated by HVT process. Antireflective coatings on polymer substrates have received significant attention for their potential applications. In this paper, robust microporous antifogging antireflective coatings on polymer substrates were prepared from acid-catalyzed silica sol followed by hydrochloric acid vapor solidification at mild temperature below glass transition temperatures of common polymers. The coatings passed 3H pencil hardness test, sand flow test and water-drop test. They had excellent antireflective and antifogging properties. The maximum transmittance of coatings on PMMA substrates reached 100.0% (the maximum transmittance wavelength could be regulated) and average transmittance reached 99.0% in 400–800 nm. The advantage and mechanism of hydrochloric acid vapor solidification and mechanical strength enhancement of coatings are discussed in contrast to ammonia vapor treatment and air vapor treatment. The hydrochloric acid vapor treatment results in a dense integrated microporous film structure. Optical properties were characterized by a UV–Vis spectrophotometer. Surface wettability was studied by a contact angle/interface system. Surface morphologies and structures of coatings were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and atom force microscopy (AFM). Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2015 |

