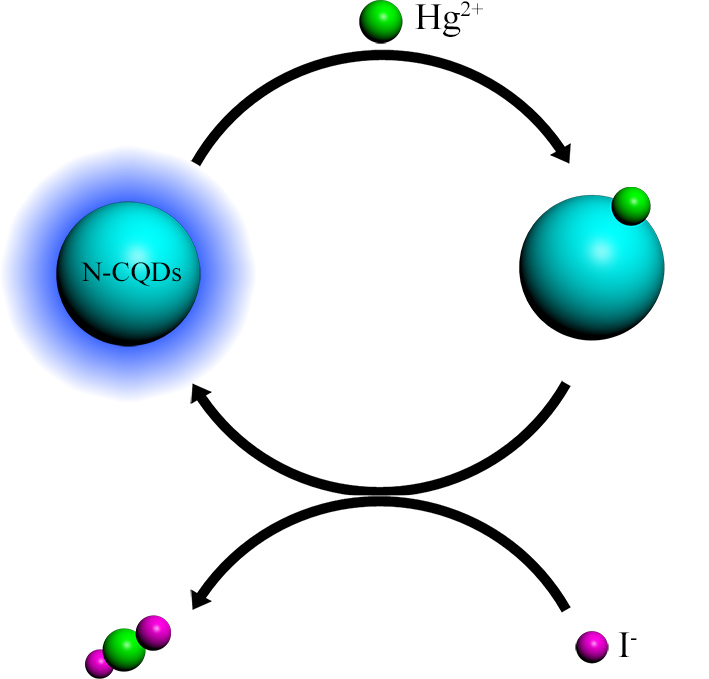
Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots (N-CQDs) with strong blue fluorescence and a high quantum yield of 66.8% were synthesized via a facile one-pot hydrothermal treatment with ammonium citrate and ethylenediamine as carbon and nitrogen sources, respectively. The blue fluorescence emission is independent of the excitation wavelengths and is very stable in a wide pH range. These N-CQDs, dispersed well in water and other polar solvents, showed a highly selective and sensitive detection of hazardous and toxic Hg2+ in the range of 10 nM to 20 μM through a fluorescence quenching process. The N-CQDs quenched by Hg2+ exhibited high selectivity and sensitivity for I− in the range of 0.5 μM to 40 μM via a fluorescence recovery process. A possible charge transfer process responsible for the effective detection was proposed according to the UV-vis absorption and fluorescence decay measurements.
Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2 015

