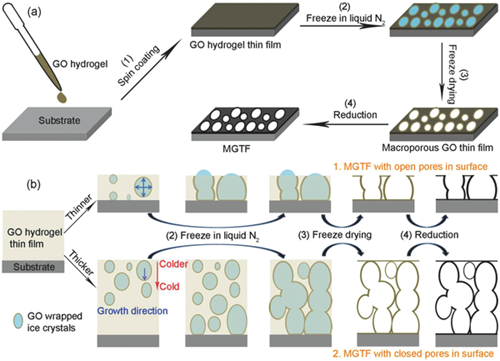
a) Preparation of the MGTFs; b) schematic illustration of the ice crystal-induced phase separation process for preparation of MGTFs. It is indicated that different types of macropores are formed in the surfaces of the MGTFs due to different thicknesses of the GO hydrogel thin films.
Graphene sheets have been demonstrated to be the building blocks for various assembly structures, which eventually determine the macroscopic properties of graphene materials. As a new assembly structure, transparent macroporous graphene thin films (MGTFs) are not readily prepared due to the restacking tendency of graphene sheets during processing. Here, an ice crystal-induced phase separation process is proposed for preparation of transparent MGTFs. The ice crystal-induced phase separation process exhibits several unique features, including efficient prevention of graphene oxide restacking, easy control on the transparency of the MGTFs, and wide applicability to substrates. It is shown that the MGTFs can be used as porous scaffold with high conductivity for electrochemical deposition of various semiconductors and rare metal nanoparticles such as CdSe, ZnO, and Pt, as well as successive deposition of different materials. Notably, the macroporous structures bestow the MGTFs and the nanoparticle-decorated MGTFs (i.e., Pt@MGTF and CdSe@MGTF) enhanced performance as electrode for oxygen reduction reaction and photoelectrochemical H2 generation. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015 |

