The direct and controlled activation of a C(sp3)[BOND]H bond adjacent to an O atom is of particular synthetic value for the conventional derivatization of ethers or alcohols. In general, stoichiometric amounts of an oxidant are required to remove an electron and a hydrogen atom of the ether for subsequent transformations. Herein, we demonstrate that the activation of a C[BOND]H bond next to an O atom could be achieved under oxidant-free conditions through photoredox-neutral catalysis. By using a commercial dyad photosensitizer (Acr+-Mes ClO4?, 9-mesityl-10-methylacridinium perchlorate) and an easily available cobaloxime complex (Co(dmgBF2)2?2?MeCN, dmg=dimethylglyoxime), the nucleophilic addition of β-keto esters to oxonium species, which is rarely observed in photocatalysis, leads to the corresponding coupling products and H2 in moderate to good yields under visible-light irradiation. Mechanistic studies suggest that both isochroman and the cobaloxime complex quench the electron-transfer state of this dyad photosensitizer and that benzylic C[BOND]H bond cleavage is probably the rate-determining step of this cross-coupling hydrogen-evolution transformation. Chemistry–A European Journal, 2015 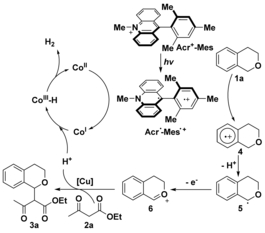
Plausible mechanism. |

