Inverted hybrid organic solar cells based on pairs of donor and acceptor materials offer an enhanced light absorption width and charge collection. Although recent developments lead to a demonstrated power conversion efficiency (PCE) of over 4% for such devices; basic underlying phenomena are still under investigation. In order to understand role of introducing nanoparticles in inverted hybrid solar cells, devices with various weight ratios of P3HT, CuO, PCBM and ZnO were prepared. The addition of CuO and ZnO improved the PCE of the P3HT:PCBM solar cells. The incorporation of nanoparticles were found to enhance the absorption and also increase the surface roughness of the active layer. The CuO and ZnO nanoparticles agglomerated as their ratio relative to P3HT and PCBM increased and completely aggregated in the absence of conjugated polymer and fullerene derivative. Synthetic Metals, 2015 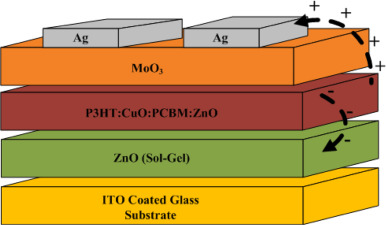
Schematic diagram of inverse geometry hybrid organic solar cells. |

