Solid silica nanoparticles (ca. 20 nm), hollow silica nanoparticles (ca. 60 nm) and a binder solution composed of silica nanosheets and acid-catalyzed silica sol were used to fabricate superamphiphobic coatings with high transmittance and excellent robustness via a sequential combination of easy dip-coating and spray-coating processes. The water contact angle (WCA) and ethylene glycol contact angle (OCA) of the coating were 171° and 150°, respectively. The maximum transmittance of coated glass reached 96.2% at the wavelength of 550 nm, which is much higher than that of blank glass (91.2%). The coatings demonstrated excellent mechanical robustness. They fell at the 5A level in a tape adhesion test based on ASTM D3359-93, and could endure a 5H pencil scratching test. They also retained their superhydrophobicity after tape peeling test, sand abrasion test, water drop-impact test, and outdoor durability test for five months. Royal Society of Chemistry, 2015 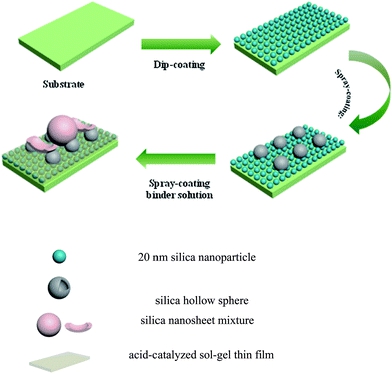
Schematic illustration for the fabrication and structure of coatings. |

