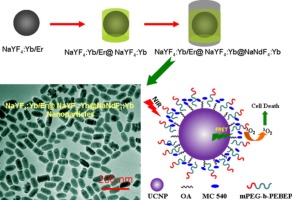
Upconversion (UC) nanostructures have attracted much interest for their extensive biological applications. In this work, we describe a sequential synthetic route to prepare sandwiched NaYF4:Yb/Er@NaYF4:Yb@NaNdF4:Yb core–shell upconversion nanoparticles. The as-prepared products were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEM 2100F), respectively. The as-prepared core–shell nanoparticles of NaYF4:Yb/Er@NaYF4:Yb@NaNdF4:Yb are composed of elliptical nanoparticles with a length of 80 nm and width of 42 nm, which show efficient upconversion fluorescence excited at 808 nm indicating the formation of core–shell–shell sandwiched nanostructures. In addition, the as-prepared sandwiched NaYF4:Yb/Er@NaYF4:Yb@NaNdF4:Yb core–shell upconversion nanoparticles also show strong upconversion fluorescence excited at 980 nm. Amphiphilic mPEG2k-b-PEBEP6Kcopolymers (denoted as PPE) were chosen to transfer these hydrophobic UCNPs into the aqueous phase for biological application. In vitro photodynamic therapy of cancer cells show that the viability of cells incubated with the nanoparticles loaded with MC 540 was significantly lower as compared to the nanoparticles without photosensitizers exposed to NIR laser. Applied Surface Science, 2015 |

