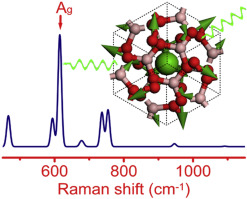
Ba2Pb(B3O6)2 polycrystalline powder was synthesized by a solid state reaction using BaCO3, Pb3O4 and H3BO3 as initial reactants. The crystal structure was solved from the powder X-ray diffraction data by the Rietveld refinement method and the DFT (density functional theory) calculation. The results show that Ba2Pb(B3O6)2 is isostructural with the high-temperature phase BaB2O4 (Ba2Ba(B3O6)2). It crystallizes in the trigonal space groupR 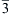 c with a = b = 7.20295(3) Å, c = 37.594(1) Å, and Z = 6. The structure is built up of the layers of B3O6 rings that are separated by Ba2+ or Pb2+ cations. The Raman spectrum of Ba2Pb(B3O6)2 was interpreted on the basis of the analysis through site group method. Its irreducible representation of the normal modes is 10A1g + 11A2g + 10A1u + 11A2u + 21Eg + 21Eu among which 10A1g + 11A2g + 10A1u + 10A2u + 21Eg + 20Eu are optical modes, where the A1g and Egare Raman active. The DFT calculated results confirmed the results of the site group analysis and assigned all peaks in the experimental Raman spectrum. The α-BaB2O4Raman spectrum was recorded and compared with the Ba2Pb(B3O6)2 Raman spectrum. The effect of the Pb2+ cations on the Raman intensity was discussed. c with a = b = 7.20295(3) Å, c = 37.594(1) Å, and Z = 6. The structure is built up of the layers of B3O6 rings that are separated by Ba2+ or Pb2+ cations. The Raman spectrum of Ba2Pb(B3O6)2 was interpreted on the basis of the analysis through site group method. Its irreducible representation of the normal modes is 10A1g + 11A2g + 10A1u + 11A2u + 21Eg + 21Eu among which 10A1g + 11A2g + 10A1u + 10A2u + 21Eg + 20Eu are optical modes, where the A1g and Egare Raman active. The DFT calculated results confirmed the results of the site group analysis and assigned all peaks in the experimental Raman spectrum. The α-BaB2O4Raman spectrum was recorded and compared with the Ba2Pb(B3O6)2 Raman spectrum. The effect of the Pb2+ cations on the Raman intensity was discussed. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2015 |

