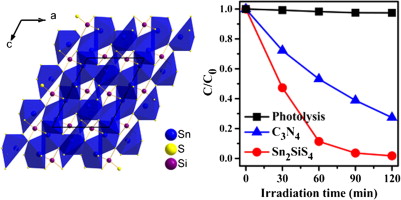
The new ternary sulfide Sn2SiS4 has been synthesized via high-temperature solid state reaction. It crystallizes in the centrosymmetric space group P21/c of the monoclinic system. In the structure, the Sn2+ cations are coordinated to a heavily-distorted octahedron of six S atoms or a pentagonal pyramid of six S atoms, both geometries clearly demonstrating the effect of the stereo-chemically active electron lone pair on the Sn coordination environment. These SnS6 polyhedra and the SiS4 tetrahedra are connected to each other via corner and edge-sharing to generate a three-dimensional framework. Based on the diffuse reflectance measurement and the electronic structure calculation, Sn2SiS4has an indirect band gap of 2.00 eV. Interestingly, Sn2SiS4 exhibits an efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity pertaining to Rhodamine B (RhB) degradation, which is superior to the important photocatalyst C3N4. Moreover, the photocatalytic mechanism was also elucidated based on the active species trapping experiments. Optical Materials, 2015 |

