A fast and accurate numerical method of solving bioheat transfer problems is critical for many biomedical applications, such as efficient implementation of thermal therapy planning in a clinical setup, and evaluation of the thermal effects induced by specific energy absorption rate (SAR) from external electromagnetic field. This paper developed a parallel finite-difference method based on alternating direction explicit (ADE) scheme to solve three dimensional transient bioheat equation for the realistic tissue structure. An optimized processing pipeline for accurate presentation of the irregular boundary condition was established to considerably reduce the staircase errors induced by cubic voxel. The voxels order aligned along diagonal direction was designed to allow fast parallel strategy for the lower and upper matrix solution involved in ADE scheme for irregular tissue. The test cases including a real head model have indicated that the developed method can support large time step and cubic voxel approximation of irregular interface and boundary, and also produce significant parallel efficiency. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer Volume 95, April 2016, Pages 843–852 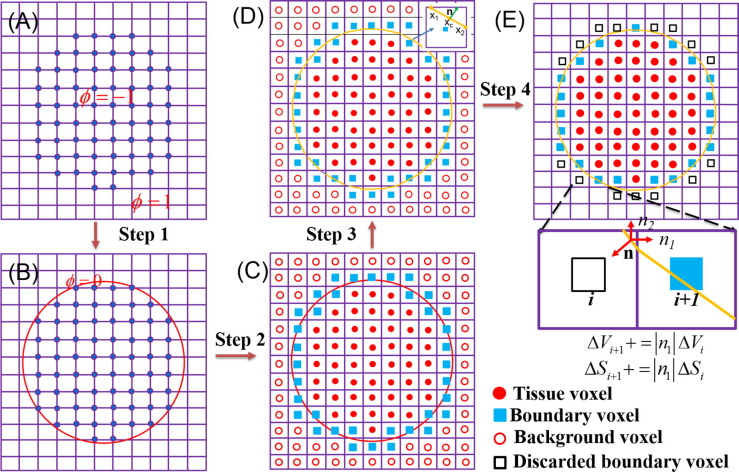
The schematic diagram of optimized processing pipeline for boundary condition: (A) the binary mask for each tissue determined based on labeled voxels according to tissue type; (B) the tissue structure represented by the smooth index; (C) the voxels classified as three type: tissue voxel, background voxel and boundary voxel; (D) the intersection surface estimated by isosurface of ϕ = 0 for each boundary voxel; (E) the active boundary rearrangement. |

