A new multilayer gas adsorption model is built based on the GAB (Guggenheim-Anderson-de Boer) model and L-F isotherm (Langmuir-Freundlich isotherm). Accounting for the heterogeneity of the adsorption system, the adsorption rate is assumed to be α th power of the surface area as demonstrated in L-F isotherm; the modified GAB model has the same form as that of the GAB equation with the difference lying on the relative pressure form; the nominal relative pressure is the α th power of the relative pressure. Different adsorption isotherm models are applied to correlate the adsorption data of microporous materials. The modified GAB model has the best conformity with the experimental data and can get almost the same so called “BET monolayer capacity” with that of the original BET equation using consistence criteria. The parameters in the modified GAB model were calculated as well; the non-unity of α indicated that the heterogeneity of the adsorption system is un-negligible even on the highly homogeneous surface.
Separation and Purification Technology
Available online 19 January 2016
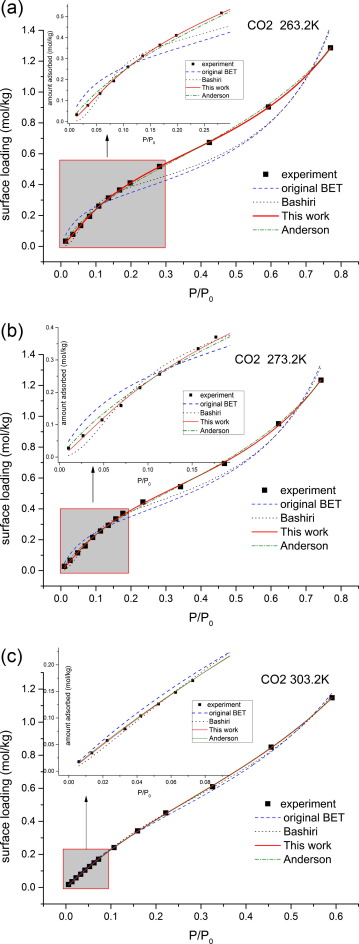
Comparison of model prediction with experimental data for CO2 adsorption on graphitized carbon black. Fig. (a), (b) and (c) represents adsorption at 263.2K, 273.2K 303.2K respectively. Black squares represent experimental data. Blue dash line represents the data predicted by BET model[2]; black dot line represents the data predicted by Bashiri[11]; Red solid line represents the data predicted by the modified GAB model built in this work; Oliva dash dot line represents the data predicted by the GAB model.

