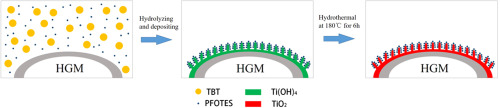
The super-hydrophobic and IR-reflectivity hollow glass microspheres (HGM) was synthesized by being coated with anatase TiO2 and a super-hydrophobic material. The super-hydrophobic self-cleaning property prolong the life time of the IR reflectivity. TBT and PFOTES were firstly applied and hydrolyzed on HGM and then underwent hydrothermal reaction to synthesis anatase TiO2 film. For comparison, the PFOTES/TiO2 mutual-coated HGM (MCHGM), PFOTES single-coated HGM (F-SCHGM) and TiO2 single-coated HGM (Ti-SCHGM) were synthesized as well. The MCHGM had bigger contact angle (153°) but smaller sliding angle (16°) than F-SCHGM (contact angle: 141.2°; sliding angle: 67°). Ti-SCHGM and MCHGM both showed similar IR reflectivity with ca. 5.8% increase compared with original HGM and F-SCHGM. For the thermal conductivity, coefficients of F-SCHGM (0.0479 W/(m·K)) was basically equal to that of the original HGM (0.0475 W/(m·K)). Negligible difference was found between the thermal conductivity coefficients of MCHGM-coated HGM (0.0543 W/(m·K)) and Ti-SCHGM (0.0546 W/(m·K)). Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids Available online 4 June 2016 |

