Mn4CaO5 cluster as a natural oxygen-evolving complex, plays an important role in Photosystem II to effectively oxidize water molecules. Corner-oxo and μ-oxo bridge connect the cuboidal Mn3CaO4 unit and the manganese atom, that was considered to be the significant component in natural oxygen-evolving process. Polynulear metal-based clusters with cubane cores seize researcher’s eyeballs for their similar active site with natural Mn4CaO5. However, copper catalysts were rarely studied for the oxygen evolution simulation.
Prof. Lizhu Wu’s group from Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences designed biomimetic molecular cubane copper catalysts ([(LGly-Cu)4] and [(LGlu-Cu)4]) for water oxidation. Schiff base (3-methoxy-salicylidene)-amino acid (glycine, glutamic acid) chelates was selected to coordinate copper(II) ion. The turnover frequency of electrocatalytic water oxidation is 267 s-1 for [(LGly-Cu)4] at 1.70 V and 105 s-1 for [(LGlu-Cu)4] at 1.56 V. The synergy and the successive two-electron transfer processes involved in the tetranuclear copper cubane centers are the key factor to the high performance of the catalysts. The study of the biomimetic copper-based catalysts is believed to further promote the investigation of successive electron transfer and the design of more active water-oxidation catalysts.
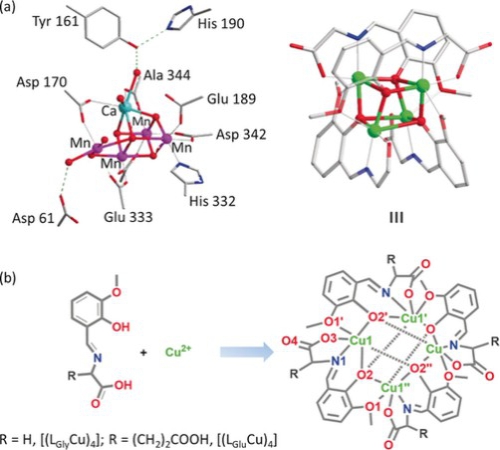
Figure. a) Structures of the OEC in PSII. b) Synthesis of [(LGly-Cu)4] and [(LGlu-Cu)4].
The study entitled “A Bio-inspired Cu4O4 Cubane: Effective Molecular Catalysts for Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation in Aqueous Solution” has been published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
Link: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201803944
E-mail: lzwu@mail.ipc.ac.cn

