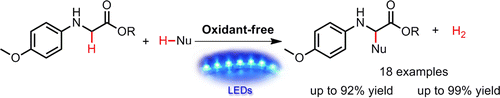
Visible light catalysis assisted site-specific modification of α-amino acids by C–H bond functionalization without the use of any oxidant or base is described. Using Ru(bpy)3(PF6)2and Co(dmgH)2pyCl as a photosensitizer and a catalyst, respectively, a variety of glycine esters with β-keto esters or indole derivatives can be quantitatively converted into the desired cross-coupling products and hydrogen (H2) in good to excellent yields under visible light irradiation. A mechanistic study reveals that the cascade electron transfer processes from glycine ester to the photoexcited Ru(bpy)3(PF6)2 and then to Co(dmgH)2pyCl catalyst, together with the capture of protons delivered by substrates, are crucial for the cross-coupling hydrogen evolution reaction of secondary amines in organic solvents. ACS Catal., 2015 |

